On August 26, 2025, the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE) hosted a major cybersecurity event at Taipei 101 — “Promoting Zero Trust Adoption in Securities Firms – Application Protection.” More than 110 security officers and IT specialists from brokerage firms attended, underscoring the urgency of strengthening defenses across Taiwan’s financial market. The core message focused on the following: applying the Zero Trust framework to reduce risks and prevent hackers from exploiting system gaps.
Why Zero Trust, and why now? Zero Trust means “never trust, always verify”: continuously authenticate users and devices, and validate sensitive actions based on risk and context—on-prem or remote. TWSE’s 2025 seminar series translates FSC’s 2024 Zero Trust guidance into practical steps, strengthening market resilience and investor confidence.
In this article, we’ll break down the Zero Trust concept in simple terms. Even if you’re not familiar with cybersecurity or technical jargon, you’ll understand why this movement marks a crucial step in protecting accounts, assets, and the overall resilience of the financial market.
1. TWSE Pushes for Zero Trust Adoption Among Securities Firms
Core Principle: Application Protection
The TWSE emphasized that applications are the true entry points of digital infrastructure. Think about your stock trading platform, mobile banking app, or internal management system—all of these are applications. If they are compromised, it’s as if the vault doors of the financial system were left wide open.
That’s why one of the key pillars of Zero Trust is securing applications themselves. Instead of relying solely on traditional protections like passwords or firewalls, securities firms are being asked to implement more advanced security mechanisms to safeguard financial operations.
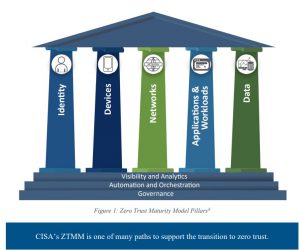
2. What Is Zero Trust and Why Now?
For those who aren’t tech-savvy, “Zero Trust” may sound complex, but its core idea is actually very simple:
- Never automatically trust any user or device.
- Verify security at every login and every action.
Traditional Security vs. Zero Trust
Think of traditional cybersecurity like a company lobby with a security guard at the entrance. If you have an employee badge (a username and password), you’re allowed in—and once inside, no one questions you further. This model is risky in today’s world, where hackers use increasingly sophisticated methods to bypass a single checkpoint.
Zero Trust takes a different approach. Its philosophy is: “Never trust, always verify.” Whether you’re an employee on the company network using a company-issued device, or an outsider accessing remotely, the system does not automatically trust you. Every access attempt must be continuously validated.
Why the Taiwan Stock Exchange Is Promoting Zero Trust
- Rising cyber threats: The financial market is one of the most attractive targets for hackers. A single breach can lead to enormous losses.
- Limitations of traditional defenses: Firewalls and passwords alone can’t protect against modern threats such as phishing, credential theft, or insider misuse.
- Global regulatory momentum: In recent years, U.S. and EU regulators have strongly advocated for Zero Trust adoption across both government and financial institutions. Taiwan is now following this trend to strengthen its overall market resilience and investor confidence.
👉 Want to dive deeper into the concept? Check out our guide: What Is Zero Trust Architecture? Why Every Business Needs a Zero Trust Strategy in 2025
3. Key Zero Trust Technologies
At the conference, the Taiwan Stock Exchange highlighted several core technologies that securities firms should adopt. Here’s a plain-language breakdown:
- Least Privilege Access
👉 Give users only the minimum permissions they need.
Example: A customer service agent doesn’t need the ability to delete client transaction records. Limiting access reduces the chance of misuse or damage if an account is compromised. - Just-in-Time (JIT) Access
👉 Access rights are granted only when necessary, not permanently.
Example: An engineer fixing a system gets temporary admin privileges during the task. Once the work is done, those privileges are immediately revoked. - User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
👉 The system learns normal user behavior and flags anomalies.
Example: If you usually log in from Taipei during the day, but suddenly log in from overseas at midnight, the system will trigger an alert. - Secure Software Development & CI/CD Automation
👉 Ensures software updates and deployments are free from vulnerabilities.
Example: During app upgrades, automated checks prevent hackers from injecting malicious code into new versions. - Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP)
👉 Think of RASP as an immune system for applications. It monitors activity in real time and blocks suspicious actions before they cause harm. - Risk-Adaptive Access Control
👉 Security checks adjust dynamically based on risk levels. This avoids unnecessary friction while still providing stronger safeguards in suspicious scenarios.
Example: If you log in from your usual home network in Taipei, the system may only ask for a one-time passcode. But if you log in from abroad at unusual hours, it may require facial recognition or multiple identity verifications.
4. Operate Zero Trust with SIEM, SOC, and SOAR
TWSE emphasized Zero Trust must integrate with SIEM (visibility), SOC (24/7 operations), and SOAR (automated response).
1. SIEM – Security Information and Event Management
Think of SIEM as the “monitoring brain.” It collects and analyzes security events across systems—such as unusual logins or suspicious activity—to provide a centralized view of potential threats.
2. SOC – Security Operations Center
The SOC is the control tower of cybersecurity. It combines human experts and monitoring tools to watch over systems 24/7, ready to respond the moment something unusual happens.
3. SOAR – Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response
Despite the long name, SOAR is simply about automated response. For example, if SIEM detects a hacking attempt, SOAR can instantly block the suspicious account or IP address without waiting for manual action.
When combined with Zero Trust, these three components form a comprehensive defense network—making it much harder for hackers to find weaknesses or slip through unnoticed.
5. Why This Matters for Investors
At this point, you might be wondering: “All these technologies sound highly technical—how does this affect me as an individual investor?”
The truth is, these security measures directly protect your accounts, your stocks, and your money.
1. Prevent Account Takeover
Zero Trust prevents hackers from impersonating you—or even employees with privileged access. For example, if someone steals your password but logs in from an unusual location, the system will block access. Similarly, if a hacker attempts to use an employee account to access your information, the system can stop them in real time.
2. Reduce Platform Downtime Risks
Coordinated detections and automated playbooks help contain disruptions faster, reducing trading downtime risk.
3. Enhance Market Trust
Frequent cybersecurity incidents erode investor confidence. By promoting Zero Trust, the Taiwan Stock Exchange aims to make the financial market more reliable and resilient, which can also attract more international investment.
Keypasco ZTNA
Keypasco ZTNA is a cybersecurity solution built on Zero Trust Network Access principles. Developed in line with U.S. NIST and CISA standards, as well as Taiwan’s government Zero Trust framework, it is certified by the National Institute of Cyber Security. Keypasco ZTNA employs identity verification, device authentication, and trust inference technologies to help organizations achieve comprehensive and robust cybersecurity protection.
- Identity Verification: Offers multi-factor authentication, including FIDO U2F and FIDO2 solutions.
- Device Authentication: Scans device attributes and software information, storing them on Keypasco servers for device validation.
- Trust Inference: Uses artificial intelligence to analyze behavior, continuously assess risk, and trigger additional authentication when needed.
Keypasco meets global standards and is trusted by government, finance, healthcare, smart building, and high-tech organizations worldwide. As cyber threats evolve, we remain committed to empowering organizations with robust, future-ready security solutions. This ensures that they stay compliant, resilient, and ahead of the curve in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Looking to implement Zero Trust but unsure where to start?
👉 Contact our cybersecurity experts today to learn how your financial institution can strengthen defenses and protect investor accounts.