“A recent discovery revealed a major vulnerability in McDonald’s AI-driven hiring platform, potentially exposing the personal data of up to 64 million applicants. As businesses rapidly deploy AI across operations—from HR and customer service to marketing—the drive for efficiency often outpaces rising security risks
Despite its power, AI is rapidly becoming a lucrative target for cybercriminals
This article examines the McDonald’s data breach, uncovers the hidden cybersecurity risks tied to AI adoption, and offers actionable steps, such as implementing MFA and Zero Trust architecture, to help organizations strengthen their defenses.
1. What Happened: McDonald’s AI Hiring Platform Hacked in Just 30 Minutes, Exposing 64 Million Applicant Records
What Platform Was Breached?
The breach targeted “Olivia,” an AI-powered recruitment assistant developed by Paradox.ai for McDonald’s. Olivia is designed to streamline the hiring process by interacting with job applicants, collecting their contact information and resumes, and scheduling interviews—all before they take personality assessments. The platform operates under the domain McHire.com and plays a central role in McDonald’s global recruitment strategy.
How Did the Hackers Get In?
On June 30, cybersecurity researchers Ian Carroll and Sam Curry discovered a critical vulnerability while probing the backend of McDonald’s recruitment system. Astonishingly, the researchers accessed the admin panel using default credentials—‘123456’ as both username and password. Even more concerning, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) was disabled. Even more alarming, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) was not enabled.
This allowed them to access the admin dashboard as if they were Paradox team members—with full backend privileges and unrestricted access to applicant data.
But the flaws didn’t stop there
They also discovered an IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference) vulnerability in the API, enabling access to any applicant’s full profile and chat history merely by altering the applicant ID in the request y, including timestamps, preferred work shifts, and even personality test results.
What Data Was Exposed?
According to the researchers, the vulnerability made it easy to access highly sensitive applicant information, including:
- Full names, email addresses, and phone numbers
- Job application details such as position, location, and submission time
- Complete chat transcripts with the AI assistant Olivia, including answers to screening questions and resume details
Based on their estimates, the breach may have affected as many as 64 million records, posing a serious risk to personal privacy and data security.
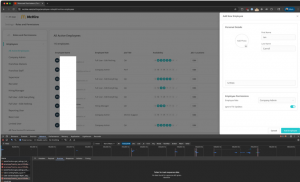
Source: Ian Carroll’s blog
How Did Paradox Respond?
Paradox.ai stated that the vulnerability was patched on the same day it was reported by the researchers. The company also claimed that only a small portion of applicant data was exposed and that the issue had not been previously exploited by others.
However, the cybersecurity community was stunned that a platform handling tens of millions of personal records lacked even the most basic protections—no multi-factor authentication, no brute-force protection, and default admin credentials still active.
2. The Hidden Security and Privacy Risks of AI Tools
While AI platforms offer major efficiency gains, they’re also becoming prime targets for cyberattacks. Here’s why:
⚠️ 1. AI Platforms Collect Massive Amounts of Sensitive Data
AI systems don’t just store names and phone numbers—they often contain resumes, cover letters, personal preferences, and even behavioral or personality assessments. When leaked, this kind of data can be more damaging than stolen credit card info. The risks include:
- Precision-targeted phishing attacks
- Identity theft and fraudulent account creation
- Social engineering scams
- Insider fraud (e.g., fake recruiters or interviews)
⚠️ 2. Common API Vulnerabilities Like IDOR
IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference) is a frequent flaw in fast-moving SaaS and AI platforms. It occurs when access control on object references (like user IDs) is not properly enforced. For example, simply changing a URL from “/applicant/123” to “/applicant/124” could expose someone else’s data.
⚠️ 3. Weak Credentials and Test Environments Left Behind
Researchers suspect that McDonald’s backend used a weak default password—likely a remnant of an old test environment or an unmodified default configuration. This is a common pitfall when deploying SaaS platforms quickly, and to attackers, it’s like finding a front door left wide open.
3. How Can Companies Reduce AI-Related Security Risks?
Five Best Practices for Safer AI Integration
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA is the most basic yet critical defense against credential-based attacks. Without it, even the most sophisticated system can be compromised with a simple username-password combo.
Implementation Tips:
- Use TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Passwords) or hardware security keys like YubiKey
- Require MFA not only for employee logins but also for backend systems and API access
- Ensure administrators cannot bypass MFA, even for internal operations
- Implement a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” This means that even internal users must be subject to strict access controls and continuous monitoring—an essential approach when dealing with sensitive AI systems.
How to Apply Zero Trust:
- Require identity verification and risk assessment for every data access request
- Enforce role-based authorization and session validation for all API calls
- Eliminate the use of “super admin” accounts; instead, apply least privilege access, ensuring each user only has the permissions they absolutely need
Not sure where to start with Zero Trust? Don’t worry!
Keypasco ZTNA is a cybersecurity solution built on Zero Trust Network Access principles. Developed in line with U.S. NIST and CISA standards, as well as Taiwan’s government Zero Trust framework, it is certified by the National Institute of Cyber Security. Keypasco ZTNA employs identity verification, device authentication, and trust inference technologies to help organizations achieve comprehensive and robust cybersecurity protection.
- Identity Verification: Offers multi-factor authentication, including FIDO U2F and FIDO2 solutions.
- Device Authentication: Scans device attributes and software information, storing them on Keypasco servers for device validation.
- Trust Inference: Uses artificial intelligence to analyze behavior, continuously assess risk, and trigger additional authentication when needed.
Keypasco meets global standards and is trusted by government, finance, healthcare, smart building, and high-tech organizations worldwide. As cyber threats evolve, we remain committed to empowering organizations with robust, future-ready security solutions. This ensures that they stay compliant, resilient, and ahead of the curve in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
- Strengthen Supply Chain and Third-Party Security Audits
As demonstrated by the McDonald’s incident involving the vendor Paradox.ai, companies must enforce strict cybersecurity standards when working with AI and SaaS providers.
Key Audit Criteria:
- Compliance with industry-recognized certifications such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2 Type II
- Support for Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Zero Trust principles
- Clear incident reporting protocols and enforceable penalty clauses
- Implement Vulnerability Scanning and Bug Bounty Programs
Many security flaws can be detected early through automated scanning tools or by engaging ethical hackers before malicious actors exploit them.
Development teams should adopt the mindset that “security is part of the code.” Regular penetration testing, permission audits, API security testing, and password checks should be integral to the software development lifecycle.
4. Conclusion: AI Is Not Immune—Security Must Keep Pace with Innovation
The McDonald’s AI data breach serves as a stark reminder that even global giants can expose millions of records over something as simple as a “123456” password. While AI tools offer incredible efficiency, neglecting basic cybersecurity measures can lead to devastating consequences.
Starting today, companies should focus on:
- Implementing MFA and robust access management
- Adopting a Zero Trust security framework
- Strengthening vendor security audits
- Conducting regular penetration testing and risk assessments
- Promoting a strong security culture and training
In the digital race ahead, success isn’t just about innovation—it’s about trust and safety. Cybersecurity is the moat that protects a company’s reputation.