Don’t Assume 2FA Makes You Safe! Hackers Have Evolved — Here’s Why MFA Is a Smarter Move
As awareness of online security grows, more users are enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) on their digital accounts. Whether it’s for social media, online banking, or shopping platforms, many services now recommend turning on 2FA to protect your personal data.
But here’s the question:
But does enabling 2FA truly make your account secure?
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, relying solely on 2FA is no longer enough to prevent modern phishing scams. Hackers have developed advanced methods to bypass these systems, so upgrading your protection is crucial.
What Is 2FA?
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a security process that requires users to verify their identity using two different factors before accessing an account. In addition to entering your username and password, you’ll need to provide a second piece of information to prove it’s really you.
Common types of 2FA include:
- One-Time Passwords (OTP): A short, temporary code sent via SMS, email, or generated by an authenticator app like Google Authenticator. This code is only valid for a single login attempt.
- Push Notifications: Apps like Microsoft Authenticator or Duo Mobile send a prompt to your phone asking you to approve or deny a login attempt.
- Biometric Authentication: Methods like fingerprint scans or facial recognition (Face ID) that confirm your identity using physical traits.
With 2FA, even if a hacker manages to steal your username and password, they won’t be able to access your account without the second verification step.
Is 2FA Really Enough?
Although more users are enabling 2FA, many mistakenly believe it makes their accounts completely secure. This false sense of security can lead to complacency, providing opportunities for hackers.
While 2FA does add an extra layer of protection and can slow down attackers, it cannot fully prevent advanced phishing attacks. That’s why many security experts recommend switching to multi-factor authentication (MFA) for stronger account protection.
Many users assume that receiving an OTP via SMS or approving an app notification guarantees safety. In reality, hackers can use phishing websites and real-time interception techniques to steal your verification code as soon as you enter it, allowing them to bypass 2FA entirely.
How Do Hackers Bypass 2FA? A Breakdown of Common Phishing Techniques
- Real-Time Phishing (Man-in-the-Middle Attack)
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack occurs when a hacker secretly intercepts and manipulates communication between a user and a legitimate website.
In this common phishing tactic, hackers create a fake website that looks almost identical to the real one. When a victim enters their username and password, the attacker immediately forwards these credentials to the genuine site. The real site then sends a 2FA verification prompt, which the attacker replicates on the fake site in real-time.
Once the victim inputs their 2FA code, the attacker quickly relays it to the legitimate website, successfully bypassing 2FA and gaining access to the account.
- SIM Swap Attack
In a SIM swap attack, hackers use social engineering or stolen personal data from breaches to impersonate a victim. They contact the victim’s mobile carrier and claim that their phone or SIM card is lost, requesting the phone number be transferred to a new SIM card controlled by the attacker.
Once the carrier approves the request, the hacker gains control of the victim’s phone number and can receive any one-time passwords (OTPs) sent via SMS—effectively bypassing 2FA protections that rely on text messages.
- Social Engineering Through Impersonation
Hackers often pose as customer support or IT personnel to trick users into revealing their one-time passwords (OTPs) or approving push notifications. By exploiting trust and creating a sense of urgency, attackers manipulate victims into handing over sensitive verification codes, bypassing 2FA defenses.
A More Secure Solution: MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication)
As 2FA becomes the standard security feature but continues to be compromised, both businesses and individuals are increasingly turning to a more advanced method called Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
What Is MFA?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) works similarly to 2FA but offers greater flexibility and multiple layers of verification. While 2FA requires just one additional factor beyond your username and password, MFA involves two or more extra verification factors.
These factors generally fall into three categories:
- Something You Know: Passwords, PINs, or pattern locks.
- Something You Have: Mobile devices, authenticator apps, hardware security keys.
- Something You Are: Biometric data such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans (e.g., World ID).
Unlike typical 2FA methods like OTP codes sent via SMS or app notifications, MFA can combine hardware keys, behavioral analysis (such as login location or device risk detection), and device binding to create a robust security net.
This layered approach ensures that even if hackers bypass your password and one verification step, they’ll face additional barriers blocking unauthorized access.
Why Is MFA More Secure?
- Protects Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Hardware security keys (like those following the FIDO2 standard) cannot be intercepted or relayed by phishing sites because the authentication process is tied to the specific device and legitimate website, making it impossible for fake sites to replicate the login.
- Blocks SIM Swap Attacks
By replacing SMS-based verification with mobile apps or hardware devices, attackers cannot gain access even if they intercept text messages.
- Strengthens Biometric Verification Combined with Physical Devices
Even if your password is compromised, without the physical hardware key or biometric verification like fingerprint recognition, unauthorized access is prevented.
- Dynamic Risk Assessment and Automated Blocking of Suspicious Activity
MFA systems often include real-time detection of abnormal login attempts based on unusual IP addresses, geographic locations, login frequency, or devices, automatically triggering additional verification steps or blocking suspicious activity.
Keypasco FIDO
Keypasco FIDO iKeypasco FIDO, developed by Lydsec Digital Technology, is a multi-factor authentication solution that integrates FIDO2 and FIDO UAF standards to provide a secure, passwordless login experience.
- Built on the global FIDO2 standard, it significantly reduces the burden of password management.
- Combines passwordless authentication with multiple verification factors, including device fingerprinting, geolocation, and biometric technologies, providing an enhanced level of security.
- Enables quick and secure device migration using NFC-enabled devices for seamless transfer of authentication credentials.
With Keypasco FIDO, only authorized users can log in from registered devices at specific times and locations. The system employs a patented dual-channel authentication architecture that separates login and authentication encryption channels. This design effectively blocks man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks, browser-in-the-middle (MiTB) attacks, phishing scams, and account takeover (ATO) attempts.
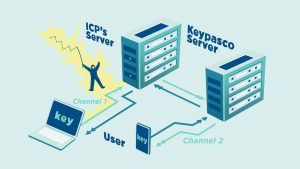
Currently, this solution is widely adopted by financial institutions and enterprises, securing millions of users with convenient, password-free access.
Although 2FA is a fundamental cybersecurity measure, it is not foolproof. As hackers evolve their tactics, relying solely on 2FA can make users vulnerable to advanced phishing attacks.
MFA integrates more diverse and harder-to-bypass verification methods—especially hardware security keys based on FIDO2, behavioral risk analysis, and biometrics—to significantly enhance digital account security. Both businesses and individuals should proactively review their account security settings and upgrade from basic 2FA to comprehensive MFA. This upgrade is key to reducing the risk of breaches and protecting valuable accounts and sensitive data.